Gluten is commonly found in wheat, barley, and rye, and is generally seen as harmless to most people. However, for some individuals, it can be a silent contributor to various health problems. The challenge lies in the fact that symptoms of gluten sensitivity are not always obvious and can often be mistaken for other conditions. Understanding how gluten affects your body can be crucial for better health management and overall well-being.
Here’s a closer look at some of the signs your body may give when reacting to gluten:
Feelings of Exhaustion and Mental Fog
One of the first noticeable effects of gluten sensitivity is a sense of persistent tiredness or what’s commonly referred to as “brain fog.” This feeling can make concentrating and thinking clearly difficult, especially after consuming foods that contain gluten. The foggy sensation can last for several hours or even a few days, hindering daily activities.

Video
Watch this video to learn about gluten intolerance, including its diagnosis, symptoms, and treatment options!
Thinning Eyelashes or Hair Loss
Many people with gluten sensitivity experience hair loss, including thinning eyelashes. This is often linked to damage to the small intestine caused by gluten, which can impair the body’s ability to absorb key nutrients such as iron, zinc, and biotin. These deficiencies are crucial for maintaining healthy hair, and a lack of them can lead to noticeable hair thinning or loss.
Digestive Discomfort
When the digestive system reacts negatively to gluten, it often results in discomfort such as bloating, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Sometimes, gluten sensitivity may also cause constipation. These digestive issues are frequently mistaken for other conditions, like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which can delay an accurate diagnosis and prolong discomfort.

Persistent Headaches or Migraines
If you notice frequent headaches or migraines, particularly after eating foods with gluten, this could be an indication of sensitivity. Gluten-triggered headaches are typically more intense and recurring, which sets them apart from regular headaches.

Unexplained Changes in Weight
Gluten intolerance can lead to unexpected changes in weight, such as sudden weight gain or loss. This can often be caused by inflammation and disruptions to metabolic processes. If you experience unexplained weight fluctuations alongside other symptoms like fatigue or digestive discomfort, it might be time to consider gluten as a possible factor.
Hormonal Fluctuations
For those with gluten sensitivity, hormone imbalances can manifest in various ways, such as irregular menstrual cycles, PMS, sleep disturbances, and unexpected weight changes. These issues are often more noticeable during important life stages, including puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Women, in particular, may experience more pronounced effects of gluten intolerance on their hormone health.
Joint and Muscle Discomfort
Joint pain and muscle aches, especially after eating gluten, are another common sign. Often described as deep, aching pain, it can affect several joints in the body, sometimes mimicking conditions like arthritis. For gluten-sensitive individuals, the inflammation caused by gluten can exacerbate joint discomfort.
Skin Irritations and Nail Health
Skin problems such as eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis herpetiformis can appear as a result of gluten sensitivity. These conditions often improve significantly once gluten is removed from the diet, highlighting the direct impact gluten can have on skin health.

Challenges with Focus and Attention
People with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) may find that their symptoms—such as short attention spans and impulsivity—are linked to gluten sensitivity. Emerging research suggests that switching to a gluten-free diet may reduce some ADHD symptoms, offering a potential solution for individuals struggling with both conditions.

Oral Health Concerns
Gluten intolerance can affect the body’s ability to absorb important nutrients like calcium, leading to oral health issues. This may result in tooth enamel sensitivity, cavities, or frequent mouth ulcers. If these dental problems persist despite good oral hygiene, gluten may be a contributing factor that should be explored.
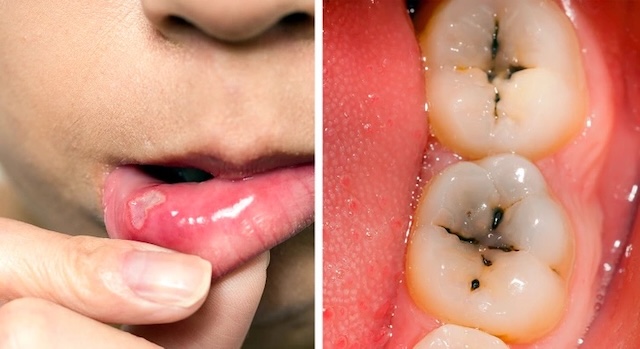
Iron Deficiency and Anemia
Celiac disease, a severe form of gluten sensitivity, can lead to iron deficiency anemia. This happens when the gluten-induced damage to the small intestine prevents the body from absorbing sufficient iron. Symptoms of this condition include fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, and joint pain.

Emotional Well-Being and Mood Shifts
Gluten sensitivity is often linked to mood disorders such as anxiety, depression, and mood swings. These emotional changes are believed to stem from the way gluten interacts with the gut-brain axis. Addressing gluten sensitivity may, in some cases, help stabilize mood and reduce emotional distress.
Autoimmune Responses and Gluten
Individuals with autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or type 1 diabetes, often have a history of gluten sensitivity. The immune system’s response to gluten can cause inflammation, which may worsen or trigger other autoimmune diseases. Managing gluten intolerance can help mitigate some of these immune system-related issues.
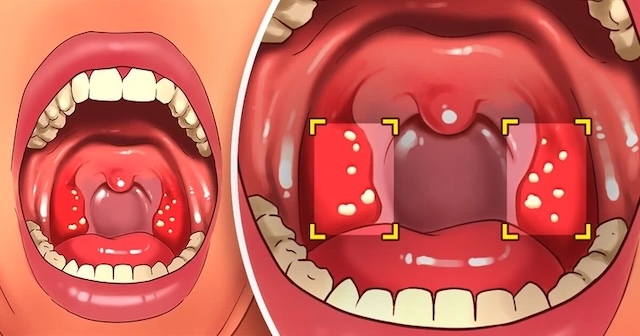
Tonsil Stones and Gluten Sensitivity
Interestingly, some individuals with gluten sensitivity report a higher frequency of tonsil stones. While this connection is not widely studied, many affected individuals notice a reduction in tonsil stone occurrences after eliminating gluten from their diet, suggesting gluten might play a role in their formation.
Hair Thinning or Loss
In addition to eyelashes, gluten sensitivity can also contribute to general hair thinning or loss. This happens when the body is unable to absorb the nutrients necessary for healthy hair growth, such as zinc, iron, and biotin, due to intestinal damage caused by gluten. A gluten-free diet has shown improvements in hair health for many individuals dealing with this issue.

Managing Gluten Sensitivity
The best way to manage gluten sensitivity is by completely eliminating gluten from your diet. Start by consulting with your doctor and requesting a blood test to check for antibodies that are commonly found in people with celiac disease. To get accurate results, it’s crucial to avoid gluten before taking the test.
Once you receive a diagnosis, removing gluten from your diet is the next step. This includes cutting out foods like wheat, rye, barley, and other gluten-containing products. Always opt for foods labeled “gluten-free” to ensure you are making safe choices.

Recognizing the signs of gluten sensitivity is essential for those who may be affected. By understanding the symptoms and making dietary adjustments, you can improve your overall health and well-being. If you suspect gluten is causing health issues, consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
Video
Watch this video to explore the differences between celiac disease and gluten sensitivity and understand which is more severe!



